定義
標準誤差(英文:Standard Error),也稱標準誤,即樣本統計量的標準差(英文:Standard Deviation),是描述對應的樣本統計量抽樣分布的離散程度及衡量對應樣本統計量抽樣誤差大小的尺度。對一個總體多次抽樣,每次樣本大小都為n,那么每個樣本都有自己的平均值,這些平均值的標準差叫做標準誤差。
標準差是單次抽樣得到的,用單次抽樣得到的標準差可以估計多次抽樣才能得到的標準誤差。
來自美國wolfram數學公司的定義:
There appear to be two different definitions of the standard error.
The standard error of a sample ofsample sizeis the sample'sstandard deviationdivided by. It therefore estimates thestandard deviationof thesample meanbased on thepopulation mean(Press et al.1992, p.465). Note that while this definition makes no reference to anormal distribution, many uses of this quantity implicitly assume such a distribution.
The standard error of an estimate may also be defined as the square root of the estimated errorvarianceof the quantity,
(Kenney and Keeping 1951, p.187; Zwillinger 1995, p.626).
公式
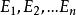 標準誤差
標準誤差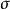 標準誤差
標準誤差設n個測量值的誤差為,則這組測量值的標準誤差等於:
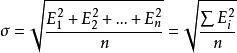 標準誤差
標準誤差其中E為誤差=測定值—真實值。
與標準差的區別
標準差與標準誤差的意義、作用和使用範圍均不同。標準差(亦稱單數標準差)一般用SD(Standard Deviation)表示,是表示個體間變異大小的指標,反映了整個樣本對樣本平均數的離散程度,是數據精密度的衡量指標;而標準誤差一般用SE(Standard error)表示,反映樣本平均數對總體平均數的變異程度,從而反映抽樣誤差的大小,是量度結果精密度的指標。
隨著樣本數(或測量次數)n的增大,標準差趨向某個穩定值,即樣本標準差s越接近總體標準差σ,而標準誤差則隨著樣本數(或測量次數)n的增大逐漸減小,即樣本平均數越接近總體平均數μ;故在實驗中也經常採用適當增加樣本數(或測量次數)使n增大的方法來減小實驗誤差,但樣本數太大意義也不大。標準差是最常用的統計量,一般用於表示一組樣本變數的分散程度;標準誤差一般用於統計推斷中,主要包括假設檢驗和參數估計,如樣本平均數的假設檢驗、參數的區間估計與點估計等。

