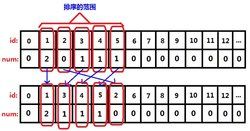
函式簡介
功 能: 使用快速排序例程進行排序
頭檔案:stdlib.h
用 法:_CRTIMP void __cdecl qsort(void*, size_t, size_t,int (*)(const void*, const void*));
參數: 1 待排序數組首地址
2 數組中待排序元素數量
3 各元素的占用空間大小
4 指向函式的指針,用於確定排序的順序
舉例
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int compare( const void *arg1, const void *arg2 );
int main( int argc, char **argv ) {
int i; /* Eliminate argv[0] from sort: */
argv++; argc--; /* Sort remaining args using Quicksort algorithm: */
qsort( (void *)argv(size_t)argc, sizeof( char * ), compare ); /* Output sorted list: */
for( i = 0; i < argc; ++i )
printf( " %s", argv[i] );
printf( "\n" );
}
int compare( const void *arg1, const void *arg2 ) { /* Compare all of both strings: */
return _stricmp( * ( char** ) arg1, * ( char** ) arg2 );
}
用法
其中base是排序的一個集合數組,num是這個數組元素的個數,width是一個元素的大小,comp是一個比較函式。
比如:對一個長為1000的數組進行排序時,int a[1000]; 那么base應為a,num應為 1000,width應為 sizeof(int),comp函式隨自己的命名。
qsort(a,1000,sizeof(int),comp);
其中comp函式應寫為:
上面是由小到大排序,return *(int *)b - *(int *)a; 為由大到小排序。
MSDN:
The qsort function implements a quick-sort algorithm to sort an array of num elements, each of width bytes. The argument base is a pointer to the base of the array to be sorted. qsort overwrites this array with the sorted elements. The argument compare is a pointer to a user-supplied routine that compares two array elements and returns a value specifying their relationship. qsort calls the compare routine one or more times during the sort, passing pointers to two array elements on each call:
以下為compare函式原型 //comp
compare( (void *) & elem1, (void *) & elem2 );
| Compare 函式的返回值 | 描述 |
| < 0 | elem1將被排在elem2前面 |
| 0 | elem1 等於 elem2 |
| > 0 | elem1 將被排在elem2後面 |
對一維數組的排序實例(從小到大排序):
對一個二維數組進行排序:
int a[1000][2]; 其中按照a[0]的大小進行一個整體的排序,其中a[1]必須和a[0]一起移動交換。//即第一行和第二行(a[0]和a[1]分別代表第一行和第二行的首地址)。使用庫函式排序的代碼量並不比用冒泡排序法小,但速度卻快很多。
對字元串進行排序
按結構體中某個關鍵字排序(對結構體一級排序):
按結構體中多個關鍵字排序(對結構體多級排序)[以二級為例]:
對結構體中字元串進行排序:
計算幾何中求凸包的Comp
相關圖片
相關圖片
 qsort
qsort qsort
qsort qsort
qsort qsort
qsort