身體活動(Physical Activity,PA)與人體健康密切相關,適當的身體活動可以降低冠心病危險因素如高血壓的發生率,而身體活動不足則可能導致能量代謝失衡,並帶來一系列的健康問題。研究PA與健康和疾病的關係,每日PA的量化分類是十分必要的。目前在國際上,普遍使用身體活動水平(Physical Activity Level,PAL)來對每日PA進行量化和分類。PAL的定義是人體24小時總能量消耗(Total Energy Expenditure, TEE)除以人體24小時的基礎能量消耗(Basal Energy Expenditure, BEE),即
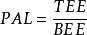 身體活動水平
身體活動水平根據PAL值的不同,身體活動的強度一般按下表分類:
| 活動狀態 | 例子 | PAL |
| 非常不活躍(Extremely inactive) | 臥床的人 | <1.40 |
| 低度(Sedentary) | 很少運動的辦公室工作人員 | 1.40-1.69 |
| 中度(Moderately active) | 每天跑步一小時的人 | 1.70-1.99 |
| 強度(Vigorously active) | 每天游泳2小時的人 | 2.00-2.40 |
| 高強度(Extremely active) | 自行陳賽手 | >2.40 |
擴展閱讀
1. Total energy expenditure (TEE) and physical activity levels (PAL) in adults: doubly-labelled water data Energy and Protein requirements, Proceedings of an IDECG workshop. United Nations University. 1994-11-04. Retrieved 2009-10-15.
2. Human energy requirements: Principles and Definitions. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2004. Retrieved 2009-10-15.
3. Human energy requirements: Energy Requirement of Adults. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2004. Retrieved 2009-10-15.
