名詞解釋
下面就英語中常見的十種基本時態進行闡述,其它的時態都是在這十種時態的基礎上結合而成的。
在語法裡,時或時態表示行為發生的時間和說話時的關係。一般分為過去式、現在式、將來式,通常也有與表示動作進行或終止的進行式和完成式等體貌一起相連用的情況。
時態連同語氣、語態、體貌和人稱為動詞形式至少可能能夠表現出的5種語法特性。
有些語言,沒有時態的使用,如分析語的中文,但必要時,仍有時間副詞的輔助。也有些語言,如日文,形容詞的詞形變化能表達出時間上的資訊,有著類似動詞的時態性質。還有些語言,如俄文,一個單詞就能表現出時態和體貌。
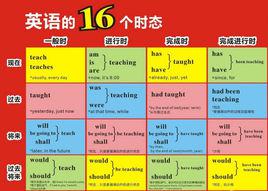
 英語時態
英語時態種類
所謂“時”就是行為發生的時段或狀態存在的時段,有完成狀態、進行狀態、完成進行狀態或一般狀態四種。由時和態結合,便形成下列十六種時態:
一般現在時,一般過去時,一般將來時,一般過去將來時;
現在 進行時,過去進行時,將來進行時,過去將來進行時;
現在 完成時,過去完成時,將來完成時,過去將來完成時;
 《英語教練》專業老師分享語法精髓
《英語教練》專業老師分享語法精髓現在 完成進行時,過去完成進行時,將來完成進行時,過去將來完成進行時.
現在時
一般現在時
1.概念:經常、反覆發生的動作或行為某種狀況。
2.時間狀語:always,usually,often,sometimes,every week (day,year,month…),once a week,on Sundays,
3.基本結構:動詞 原形 (如主語為第三人稱單數,動詞上要改為第三人稱單數形式)
4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此時態的謂語動詞若為行為動詞,則在其前加don't,如主語為第三人稱單數,則用doesn't,同時還原行為動詞。
5. 一般疑問句 :把be動詞放於句首;用助動詞do提問,如主語為第三人稱單數,則用does,同時,還原行為動詞。
6.例句:.
It seldom snows here.
He is always ready to help others.
Action speaks louder than words.
7.用法
(1)表示經常性的動作或狀態
表示經常性動作或狀態時,常與often,always,usually,sometimes,every day等時間狀語連用。如:
The shop opens at nine every day. 這家商店每天九點開門。
It seldom snows here. 這兒很少下雪。
(2)表示客觀存在或普遍真理
Light travels are faster than sound. 光速比聲速快。
Food easily goes bad in hot weather. 天氣熱時食物容易壞。(3)表示主語的特徵或狀態
The picture looks very beautiful. 這幅畫看起來很美。
Air contains oxygen and nitrogen. 空氣含有氧和氮。
(4在時間和條件狀語從句中表示將來的動作或狀態
I'll tell her about it as soon as I see her.
When does the train arrive? 火車幾點到?
(5) 用於圖片說明或劇本中的動作提示和背景說明
INSIDE THE SHELTER: Stockton slowly turns to face his wife. The angry screaming cries of the people ring in their ears even as they depart.
防空洞中:斯道克頓慢慢轉過身,面對他的妻子。那群人正在離去,而他們憤怒的尖叫聲卻還迴響在他們的耳邊。
(6) 電視節目直播解說
It's Carter to serve- he needs just one more point. He serves. And Smith misses. What a great serve!So the championshipgoes to 19-year-old Harry Carter.
該卡特發球了,他只需再得一分就贏了。他發球了,史密斯接球失誤。多漂亮的發球!冠軍屬於了19歲的哈利-卡特。
現在進行時
1.概念:表示現階段或說話時正在進行的動作及行為。
2.時間狀語:now,at this time,days,etc. look . listen
3.基本結構:be+doing
4.否定形式:be+not+doing.
5.一般疑問句:把be動詞放於句首。
6.例句:How are you feeling today?
He is doing well in his lessons.
7.用法
(1)進行時表示說話時或現階段正在進行的動作
表示現階段正在進行的動作,通常用表示現階段的時間狀語,如:today,this week,this month,this year,this term,now等。如:
He is writing a novel now. 他目前正在寫一部小說。
(2)進行時表示經常性的動作
進行時在表示經常性、重複性或習慣性的動作時必須與only,merely,simply,really,fast,rapidly,steadily,forever,all the time,always,constantly,continually,repeatedly等頻度副詞連用。如:
She is always complaining. 她總是在抱怨。
(3)進行時表示按計畫或已安排好要做的事
這一用法只適用於某些動詞,如:go,come,leave,start,arrive,return,spend,sail,meet,fly等。如:
The guest is leaving by train tonight. 客人今晚坐火車走。
(4) 補充說明
[1] 在不少情況下,表示正在進行的動作的漢語句子,並沒有“正在”這樣的字眼,但在譯為英語時必須用進行時態。如:
It's rainingheavily. 下大雨了。
How is everything going? 事情進展如何?
[2] 有些動詞通常不能用進行時。不能用進行時的動詞有:
表示感覺或感情的詞,如:hear,see,smell,taste,feel,seem,notice,hate,love,like,want,wish,refuse,prefer,forgive等。
表示存在或所屬的詞,如:exist,stay,remain,obtain,have,own,form,contain等。
表示認識或理解的詞,如:understand,know,remember,forget,believe,think,doubt等。
現在完成時
完成時的這種用法通常與由since或for引導的時間狀語連用。如:
The old man have lived here for more than twenty years.
老人已在此住了20多年了。
完成時的這種用法有時不帶時間狀語,有時可以和already,before,ever,just,lately,never,once,recently,yet等一些所指時間不具體的時間狀語連用。如:
Have you ever been to Australia? 你去過澳大利亞嗎?
[2] 有時完成時和now,today,this morning,this week,this year等的時間狀語連用。如:
I haven' t seen him today. 我今天沒見過他。
I have seen him only once this year. 我只見過他一次。
(3)完成時在時間和條件狀語從句中表示將來完成的動作
I'll go to the party as soon as (or when) I have finished my homework.
我完成作業後就去參加聚會。
(4)完成時和until now,so far,in the past few years,up to the present等表示從某時到這段時間的狀語連用 I have not heard from her so far. 到目前為止,我沒有收到過她的信。
We have learned five hundred words up to the present.到目前為止,我們已學了五百個生詞。
但要注意:當意義明確時,適用完成時的句子可以不用時間狀語。如:
He has done a lot of work. 他幹了許多工作。
She has told me about her story. 她跟我講過她的故事。
完成進行時
1.概念:表示從過去某一時間開始一直延續到的動作。這一動作可能剛剛開始,也可能仍在繼續,並可能延續到將來。
2.基本結構:have/has +been+doing
3.時間狀語:since+時間點,for+時間段等。
4.例子:I have been sitting here for an hour.
The chirdren have been watching TV since six o'clock.
5.用法
(1)完成進行時表示從過去一直持續到的動作或剛剛結束的動作
I've been writing letters all this morning.我寫了一上午信。(動作不再繼續)
O'Neil is ill. He' s been lying in the bed for three weeks.奧尼爾在病中,已臥床3個星期了。(動作會繼續下去)
(2)完成進行時表示從過去到現在的重複性動作
完成進行時的這種用法所表示的並不是一直在進行的動作,而是斷斷續續地反覆發生的動作。如:
What have you been doing all this time?你一直都在乾什麼來著?(動作可能繼續下去)
That reporter has been contributing articles to this magazine all these years.這些年那個記者一直為這家雜誌撰稿。(斷斷續續地反覆發生的動作)
過去時
一般過去時
1.概念:過去某個時間裡發生的動作或狀態;過去習慣性、經常性的動作、行為。
2.時間狀語:ago,yesterday,the day before yesterday,last week,last(year,night,month…),in 1989,just now,at the age of 5,one day,long long ago,once upon a time,etc.
3.基本結構:be動詞;行為動詞的過去式
4.否定形式:was/were+not;在行為動詞前加didn't,同時還原行為動詞。
5.一般疑問句:was或were放於句首;用助動詞do的過去式did 提問,同時還原行為動詞。
6.例句:She often came to help us in those days.
I didn't know you were so busy.
7.用法
(1)一般過去時表示過去的動作或狀態
[1]一般過去時通常與表示過去的時間狀語連用。
與一般過去時連用的時間狀語有:yesterday,last night(week,year,month,Sunday),then,at that time,at that moment,just now,a few days(weeks,months,years) ago等。例句:
Lucy turned off all the lights before she went out.
出門前露茜關了所有的燈。
[2]一般過去時也可以與today,this week(month,year)等時間狀語連用,但這些時間狀語應指過去。如:
Did you see him today? 你今天見他了嗎?(today指今天已過去的某一時刻)
[3]一般過去時還可以和for或since引導的時間狀語連用。如:
I stayed there for two months. 我在那裡呆了兩個月。
Nothing happened since then. 打那以後什麼事都沒有發生。
(2) 有時一般過去時的時間狀語或是在上下文、或是暗含於句中
Who was that? 那人是誰?
I saw Ker in town. 我在城裡看見了克爾。
(3)一般過去時在時間和條件狀語從句中表示過去將來的動作或狀態。
Hans said he would let us know if he got any news.
漢斯說要是得到訊息就告訴我們。
過去進行時
1.概念:表示過去某段時間或某一時刻正在發生或進行的行為或動作。
2.時間狀語:at this time yesterday,at that time或以when引導的謂語動詞是一般過去時的時間狀語等。
3.基本結構 s+was/were+doing
4.否定形式:s+was/were + not + doing.
5.一般疑問句:把was或were放於句首。(第一個字母大寫)
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit.
When he came in,I was reading a newspaper.
7.用法
(1)過去進行時表示過去某時正在進行的動作
[1]過去進行時通常和時間狀語連用。如:
We were having dinner when they came.他們來的時候,我們正在吃飯。
[2]過去進行時表示過去某段時間內持續的動作。如:
Carlos was staying at home all last week.上周整整一周卡洛斯都在家呆著。
They were building a dam last spring. 去年春天他們一直在修一個水壩。
[3]過去進行時表示與過去某個動作同時發生的動作。如:
I was reading while she was writing. 我在讀書,她在寫字。
[4] 有時過去進行時用於主句,位於其後的when引導的從句表示意外發生的情況:
I was walking in the street when it began to rain.我正在街上走著,突然下起了雨。
(2)過去進行時表示過去將來的動作
過去進行時的這種用法多表示過去的打算,通常僅限於come,go,leave,depart,start等一些表示移動的動詞。如:
He didn't know whether she was coming. 他不知道她是否會來。
The delegation was departing three days later. 代表團打算三天后動身。
過去完成時
1.概念:以過去某個時間為標準,在此以前發生的動作或行為,或在過去某動作之前完成的行為,即“過去的過去”。
2.時間狀語:before,by the end of last year(term,month…),etc.
3.基本結構:had + done.
基本結構:主語+had+過去分詞(done)
①肯定句:主語+had+過去分詞+其他
②否定句:主語+had+not+過去分詞+其他
③一般疑問句:Had+主語+過去分詞+其他
④特殊疑問句:特殊疑問詞+一般疑問句
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑問句:had放於句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station,the train had left.
By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books
7.用法
(1)過去完成時表示過去某時之前結束的動作或狀態
When he got there,the train had already left.他到了那兒時火車已經離開了。
Ina realized she had made a mistake.艾娜意識到她犯了個錯誤。
(2)過去完成時與when等從句連用
had+just / barely / hardly / scarcely+done...when...,no sooner...than... 是表示“剛……就……”或“不等……就……”的固定句型。如:
No sooner had we left the house than it began to rain.我們剛離開家就開始下雨了。
I had not gone much farther before I caught them up.我沒有走多遠就趕上他們了。
(3)過去完成時表示持續到過去某時之前的動作或狀態
We had finished the work by nine o'clock yesterday.昨晚九點前我們已完成了工作。
The company had completed the project by the end of 1999.到1999年底公司已完成了那個項目。
過去完成時主要表示持續到過去某時之前的動作。如:
I had been looking for it for days before I found it.這個東西,我找了好多天才找著。
The telephone had been ringing for three minutes before it was answered.電話鈴響了三分鐘才有人接。
He was tired. He'd been working all day.他累了。他工作了一整天。
After he'd been lecturing for half an hour,Professor Brown had a drink of water.布朗教授講了半小時課之後,他喝了一點水。
將來時
一般將來時
1.概念:表示將要發生的動作或存在的狀態及打算、計畫或準備做某事。
2.時間狀語:tomorrow,next day(week,month,year…),soon,in a few minutes,by…,the day after tomorrow,etc.
3.基本結構:主語+am/is/are+going to + do;will/shall + do.
4.否定形式:am/is/are not going to do ;will/shall not do。
5.一般疑問句:be放於句首;will/shall提到句首。
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies.
It is going to rain.
7.用法
(1) 基本用法
[1]一般將來時常用來表示將來時間的動作或狀況。如:
。
[2]一般將來時用於真實條件句和時間狀語從句的主句中表示將來的情況。如:
I'll tell you as soon as he comes. 他一來我就告訴你。
[3] 用於條件狀語從句表示願望或意願。如:
If you will wait for me,I shall come back soon.
如果你願意等我,我馬上就回來。
[4]一般將來時可用來表示一種傾向或習慣性動作。如:
The shop won't open until nine. 這家商店九點才會開門。
Children will be children. 孩子就是孩子。
(2) be going to +動詞原形
這一結構表示打算或準備好要做的事或有跡象表明要發生的天氣變化等情況。如:
What are you going to do during the summer holiday? 你暑假打算做什麼? The train is going to arrive. 火車就要到了。
(3)現在進行時(be +現在分詞)
有些動詞的現在進行時可以表示將要發生的動作,表示按計畫或安排即將發生的事。這類動詞有:go,come,leave,start,arrive,return,spend,sail,meet,fly等。如:
Annie is coming to supper this evening. 安妮今晚要來吃飯。
(4) be to +動詞原形
這一結構可表示約定、命令或按計畫要做的事。如:
When are they to come? 他們什麼時候來?
We are to meet at the school gate. 我們約好在校門口見。
(5) be about to +動詞原形
這一結構表示“即將做”或“馬上做”的意思。如:
He is about to leave. 他馬上就要動身。
The vacation is about to start. 假期即將開始。
將來進行時
將來進行時表示將來某一時間正在進行的動作。常表示已安排好之事,給人一種期待感。如:
What will you be doing this time tomorrow?明天這個時候你將做什麼?
The train will be leaving in a second. 火車馬上就開。
將來完成時
(1)將來完成時表示在將來某一時間之前完成的動作,往往對將來某一時間產生影響。如:
I shall have finished reading the book by the end of this week.我將在本周末前讀完這本書。
Before long,he will have forgotten all about the matter.過不久,他很快就會把這件事全然忘記。
(2)將來完成時表示持續到將來某時的動作或狀態。如:
By the time he graduates,he will have studied French for four years.到他畢業的時候,他學法語就滿四年了。
By the time Pierce comes back from the meeting,we will have waited here for three hours.到皮爾斯開會回來的時候,我們已經在這兒等了三個鐘頭了。
過去將來時
(1) 過去將來時表示過去某時之後將出現的情況,通常用於賓語從句中。如:
I thought he would come. 我以為他會來。
Jenny never imagined that she would become a doctor.詹妮從沒想到自己會當醫生。
(2) 表示從過去某時看將要發生的事情。如:
The old lady was fifty-eight then. In two years she would be sixty.老太太當時五十八歲,再過兩年就六十了。
I didn’t think they would have any objection to it.我想他們不會有什麼反對意見。
(3) 表示過去習慣性動作(不管什麼人稱都用would)。如:
Whenever he had time,Harris would go to see his grandmother.哈里斯一有時間就去看他奶奶。
Joanna would go for a walk aftershe had supper.喬安娜吃完晚飯總要去散步
轉換
方式
1.一般過去時與現在完成時的轉換 請看: A. He joined the League two years ago. B. He has been in the League for two years. C. It is two years since he joined the League. D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
2.一般現在時與現在進行時的轉換 Peter is at work,but Mike is at play. Peter is working,but Mike is playing.
3.現在進行時與一般將來時的轉換 請看: The train is leaving soon. The train will leave soon.
規則
英語中的幾種時態在一定情況下可以互相轉換,以下是幾種常見的轉換形式: