定義
平均梯度即圖像的清晰度(definition),反映圖像對 細節對比的表達能力,計算 公式為
圖像梯度: G(x,y) = dx i + dy j;
dx(i,j) = I(i+1,j) - I(i,j);
dy(i,j) = I(i,j+1) - I(i,j);
其中,I是圖像像素的值(如:RGB值),(i,j)為像素的 坐標。
圖像梯度一般也可以用中值差分:
dx(i,j) = [I(i+1,j) - I(i-1,j)]/2;
dy(i,j) = [I(i,j+1) - I(i,j-1)]/2;
圖像邊緣一般都是通過對圖像進行梯度運算來實現的。
上面說的是簡單的梯度定義,其實還有更多更複雜的梯度公式。
梯度公式
white210:
平均梯度越大,圖像層次越多,也就越清晰。其定義為:
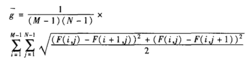 平均梯度
平均梯度式中:F(i,j)為圖像的第i行,第j列的灰度值;M、N分別為圖像的總行數和總列數。
單幅圖像的平均梯度值計算MATLAB源程式:
說明:該程式的作用是計算輸入圖像img的平均梯度值AVEGRAD
平均梯度值可以衡量圖像細節反差表達的能力,是圖形融合結果的一個評價運算元之一
function AVEGRAD=avegrad(img)
%%%% this function is used to calculate theaverage gradient of an image.
%%%%平均梯度可敏感地反映圖像對微小細節反差表達的能力,可用來評價圖像的模糊程度
%%%%在圖像中,某一方向的灰度級變化率大,它的梯度也就大。因此,可以用平均梯度值來衡量圖像的清晰度,還同時反映出圖像中微小細節反差和紋理變換特徵。
img=double(img);
[M,N]=size(img);
gradval=zeros(M,N); %%% save the gradient value of single pixel
diffX=zeros(M,N); %%% save the differential value of X orient
diffY=zeros(M,N); %%% save the differential value of Y orient
tempX=zeros(M,N);
tempY=zeros(M,N);
tempX(1:M,1:(N-1))=img(1:M,2:N);
tempY(1:(M-1),1:N)=img(2:M,1:N);
diffX=tempX-img;
diffY=tempY-img;
diffX(1:M,N)=0; %%% the boundery set to 0
diffY(M,1:N)=0;
diffX=diffX.*diffX;
diffY=diffY.*diffY;
AVEGRAD=(diffX+diffY)/2;
AVEGRAD=sum(sum(sqrt(AVEGRAD)));
AVEGRAD=AVEGRAD/((M-1)*(N-1));
