套用
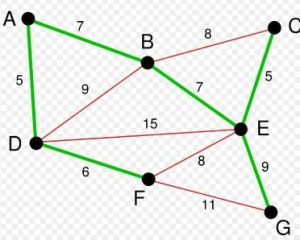 最小生成樹
最小生成樹生成樹和最小生成樹有許多重要的套用。
例如:要在n個城市之間鋪設光纜,主要目標是要使這 n 個城市的任意兩個之間都可以通信,但鋪設光纜的費用很高,且各個城市之間鋪設光纜的費用不同,因此另一個目標是要使鋪設光纜的總費用最低。這就需要找到帶權的最小生成樹。
性質
說明
最小生成樹性質:設G=(V,E)是一個連通網路,U是頂點集V的一個非空真子集。若(u,v)是G中一條“一個端點在U中(例如:u∈U),另一個端點不在U中的邊(例如:v∈V-U),且(u,v)具有最小權值,則一定存在G的一棵最小生成樹包括此邊(u,v)。
證明
為方便說明,先作以下約定:
①將集合U中的頂點看作是紅色頂點,②而V-U中的頂點看作是藍色頂點,③連線紅點和藍點的邊看作是紫色邊,④權最小的紫邊稱為輕邊(即權重最"輕"的邊)。於是,MST性質中所述的邊(u,v)就可簡稱為輕邊。
用反證法證明MST性質:
假設G中任何一棵MST都不含輕邊(u,v)。則若T為G的任意一棵MST,那么它不含此輕邊。
根據樹的定義,則T中必有一條從紅點u到藍點v的路徑P,且P上必有一條紫邊(u',v')連線紅點集和藍點集,否則u和v不連通。當把輕邊(u,v)加入樹T時,該輕邊和P必構成了一個迴路。刪去紫邊(u',v')後迴路亦消除,由此可得另一生成樹T'。
T'和T的差別僅在於T'用輕邊(u,v)取代了T中權重可能更大的紫邊(u',v')。因為w(u,v)≤w(u',v'),所以
w(T')=w(T)+w(u,v)-w(u',v')≤w(T)
即T'是一棵比T更優的MST,所以T不是G的MST,這與假設矛盾。
所以,MST性質成立。
算法描述
求MST的一般算法可描述為:針對圖G,從空樹T開始,往集合T中逐條選擇並加入n-1條安全邊(u,v),最終生成一棵含n-1條邊的MST。
當一條邊(u,v)加入T時,必須保證T∪{(u,v)}仍是MST的子集,我們將這樣的邊稱為T的安全邊。
偽代碼
GenerieMST(G){//求G的某棵MST
T〈-¢; //T初始為空,是指頂點集和邊集均空
while T未形成G的生成樹 do{
找出T的一條安全邊(u,v);//即T∪{(u,v)}仍為MST的子集
T=T∪{(u,v)}; //加入安全邊,擴充T
}
return T; //T為生成樹且是G的一棵MST
}
注意:
下面給出的兩種求MST的算法均是對上述的一般算法的求精,兩算法的區別僅在於求安全邊的方法不同。
為簡單起見,下面用序號0,1,…,n-1來表示頂點集,即是:
V(G)={0,1,…,n-1},
G中邊上的權解釋為長度,並設T=(U,TE)。
求最小生成樹的具體算法(pascal):
Prim算法
procedure prim(v0:integer);
var
lowcost,closest:array[1..maxn] of integer;
i,j,k,min:integer;
begin
for i:=1 to n do begin
lowcost[i]:=cost[v0,i];
closest[i]:=v0;
end;
for i:=1 to n-1 do begin
{尋找離生成樹最近的未加入頂點 k}
min:=maxlongint;
for j:=1 to n do
if (lowcost[j]<>0) then begin
min:=lowcost[j];
k:=j;
end;
lowcost[k]:=0; {將頂點k 加入生成樹}
{生成樹中增加一條新的邊 k 到 closest[k]}
{修正各點的 lowcost 和 closest 值}
for j:=1 to n do
if cost[k,j]
lowcost[j]:=cost[k,j];
closest[j]:=k;
end;
end;
end;
Kruskal算法
按權值遞增順序刪去圖中的邊,若不形成迴路則將此邊加入最小生成樹。
function find(v:integer):integer; {返回頂點 v 所在的集合}
var i:integer;
begin
i:=1;
while (i<=n) and (not v in vset) do inc(i);
if i<=n then find:=i else find:=0;
end;
procedure kruskal;
var
tot,i,j:integer;
begin
for i:=1 to n do vset:=i;{初始化定義 n 個集合,第 I個集合包含一個元素 I}
p:=n-1; q:=1; tot:=0; {p 為尚待加入的邊數,q 為邊集指針}
sort;
{對所有邊按權值遞增排序,存於 e中,e.v1 與 e.v2 為邊 I 所連線的兩個頂點的
序號,e.len 為第 I條邊的長度}
while p>0 do begin
i:=find(e[q].v1);j:=find(e[q].v2);
if i<>j then begin
inc(tot,e[q].len);
vset:=vset+vset[j];vset[j]:=[];
dec(p);
end;
inc(q);
end;
writeln(tot);
end;
C語言代碼
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 | #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<iostream.h> #defineMAX_VERTEX_NUM20 #defineOK1 #defineERROR0 #defineMAX1000 typedefstructArcell { double adj ; }Arcell,AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; typedefstruct { charvexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];//節點數組 AdjMatrixarcs;// 鄰接矩陣 intvexnum,arcnum;//圖的當前節點數和弧數 }MGraph; typedefstructPnode//用於 普利姆 算法 { charadjvex;//節點 doublelowcost;//權值 }Pnode,Closedge[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];//記錄頂點集U到V-U的代價最小的邊的輔助數組定義 typedefstructKnode//用於 克魯斯卡爾算法 中存儲一條邊及其對應的2個節點 { charch1;//節點1 char ch2 ;//節點2 double value ;//權值 }Knode,Dgevalue[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //------------------------------------------------------------------------------- intCreateUDG(MGraph&G,Dgevalue&dgevalue); intLocateVex(MGraphG,charch); intMinimum(MGraphG,Closedgeclosedge); voidMiniSpanTree_PRIM(MGraphG,charu); voidSortdge(Dgevalue&dgevalue,MGraphG); //------------------------------------------------------------------------------- intCreateUDG(MGraph&G,Dgevalue&dgevalue)//構造無向 加權圖 的鄰接矩陣 { inti,j,k; cout <<"請輸入圖中節點個數和邊/弧的條數:"; cin >>G.vexnum>>G.arcnum; cout<<"請 輸入節點 :"; for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i) cin>>G.vexs[i]; for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i)//初始化數組 { for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;++j) { G.arcs[i][j].adj=MAX; } } cout<<"請輸入一條邊依附的定點及邊的權值:"<<endl; for(k=0;k<G.arcnum;++k) { cin>>dgevalue[k].ch1>>dgevalue[k].ch2>>dgevalue[k].value; i=LocateVex(G,dgevalue[k].ch1); j=LocateVex(G,dgevalue[k].ch2); G.arcs[i][j].adj=dgevalue[k].value; G.arcs[j][i].adj=G.arcs[i][j].adj; } returnOK; } intLocateVex(MGraphG,charch)//確定節點ch在圖G.vexs中的位置 { inta; for(inti=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) { if(G.vexs[i]==ch) a=i; } returna; } voidMiniSpanTree_PRIM(MGraphG,charu)//普利姆算法求最小 生成樹 { inti,j,k; Closedgeclosedge; k=LocateVex(G,u); for(j=0;j j++) { if(j!=k) { closedge[j].adjvex=u; closedge[j].lowcost=G.arcs[k][j].adj; } } closedge[k].lowcost=0; for(i=1;i<G.vexnum;i++) { k=Minimum(G,closedge); cout<<"("<<closedge[k].adjvex<<","<<G.vexs[k]<<","<<closedge[k].lowcost<<")"<<endl; closedge[k].lowcost=0; for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;++j) { if(G.arcs[k][j].adj<closedge[j].lowcost) { closedge[j].adjvex=G.vexs[k]; closedge[j].lowcost=G.arcs[k][j].adj; } } } } intMinimum(MGraphG,Closedgeclosedge)//求closedge中權值最小的邊,並返回其頂點在vexs中的位置 { inti,j; doublek=1000; for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) { if(closedge[i].lowcost!=0&&closedge[i].lowcost<k) { k=closedge[i].lowcost; j=i; } } returnj; } voidMiniSpanTree_KRSL(MGraphG,Dgevalue&dgevalue)//克魯斯卡爾算法求最小生成樹 { intp1, p2 ,i,j; intbj[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];//標記數組 for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)//標記數組初始化 bj[i]=i; Sortdge(dgevalue,G);//將所有權值按從小到大排序 for(i=0;i<G.arcnum;i++) { p1=bj[LocateVex(G,dgevalue[i].ch1)]; p2=bj[LocateVex(G,dgevalue[i].ch2)]; if(p1!=p2) { cout<<"("<<dgevalue[i].ch1<<","<<dgevalue[i].ch2<<","<<dgevalue[i].value<<")"<<endl; for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++) { if(bj[j]==p2) bj[j]=p1; } } } } voidSortdge(Dgevalue&dgevalue,MGraphG)//對dgevalue中各元素按權值按從小到大排序 { inti,j; double temp ; charch1,ch2; for(i=0;i<G.arcnum;i++) { for(j=i;j<G.arcnum;j++) { if(dgevalue[i].value>dgevalue[j].value) { temp=dgevalue[i].value; dgevalue[i].value=dgevalue[j].value; dgevalue[j].value=temp; ch1=dgevalue[i].ch1; dgevalue[i].ch1=dgevalue[j].ch1; dgevalue[j].ch1=ch1; ch2=dgevalue[i].ch2; dgevalue[i].ch2=dgevalue[j].ch2; dgevalue[j].ch2=ch2; } } } } voidmain() { inti,j; MGraphG; charu; Dgevaluedgevalue; CreateUDG(G,dgevalue); cout<<"圖的鄰接矩陣為:"<<endl; for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) { for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++) cout<<G.arcs[i][j].adj<<""; cout<<endl; } cout<<"=============普利姆算法===============\n"; cout<<"請輸入起始點:"; cin>>u; cout<<"構成最小代價生成樹的邊集為:\n"; MiniSpanTree_PRIM(G,u); cout<<"============ 克魯斯 科爾算法=============\n"; cout<<"構成最小代價生成樹的邊集為:\n"; MiniSpanTree_KRSL(G,dgevalue); } |
pascal算法
kruskal
program didi;
var
a:array[0..100000] of record
s,t,len:longint;
end;
fa,r:array[0..10000] of longint;
n,i,j,x,y,z:longint;
tot,ans:longint;
count,xx:longint;
procedure quick(l,r:longint);
var
i,j,x,y,t:longint;
begin
i:=l;j:=r;
x:=a[(l+r) div 2].len;
repeat
while x>a[i].len do inc(i);
while xdec(j);
if i<=j then
begin
y:=a[i].len;a[i].len:=a[j].len;a[j].len:=y;
y:=a[i].s;a[i].s:=a[j].s;a[j].s:=y;
y:=a[i].t;a[i].t:=a[j].t;a[j].t:=y;
inc(i);dec(j);
end;
until i>j;
if i
if l
end;
function find(x:longint):longint;
begin
if fa[x]<>x then fa[x]:=find(fa[x]);
find:=fa[x];
end;
procedure union(x,y:longint);{啟發式合併}
var
t:longint;
begin
x:=find(x);
y:=find(y);
if r[x]>r[y] then
begin
t:=x;x:=y;y:=t;
end;
if r[x]=r[y] then inc(r[x]);
fa[x]:=y;
end;
begin
readln(xx,n);
for i:=1 to xx do fa[i]:=i;
for i:=1 to n do
begin
read(x,y,z);
inc(tot);
a[tot].s:=x;
a[tot].t:=y;
a[tot].len:=z;
end;
quick(1,tot);{將邊排序}
ans:=0;
count:=0;
i:=0;
while count<=x-1 do{count記錄加邊的總數}
begin
inc(i);
with a[i] do
if find(s)
begin
union(s,t);
ans:=ans+len;
inc(count);
end;
end;
write(ans);
end.
Prim
var
m,n:set of 1..100;
s,t,min,x,y,i,j,k,l,sum,p,ii:longint;
a:array[1..100,1..100]of longint;
begin
readln(p);
for ii:=1 to p do
begin
k:=0; sum:=0;
fillchar(a,sizeof(a),255);
readln(x);
m:=;
n:=[2..x];
for i:=1 to x do
begin
for j:=1 to x do
begin
read(a[i,j]);
if a[i,j]=0
then a[i,j]:=maxlongint;
end;
readln;
end;
for l:=1 to x-1 do
begin
min:=maxlongint;
for i:=1 to x do
if i in m
then begin
for j:=1 to x do
begin
if (a[i,j]
then begin
min:=a[i,j];
s:=i;
t:=j;
end;
end;
end;
sum:=sum+min;
m:=m+[t];
n:=n-[t];
inc(k);
end;
writeln(sum);
end;
end.
