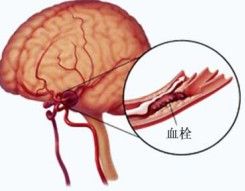
Epidemiology
China from 1986 to 1990, a large - scale population survey, the incidence was 109. 7 / 10 to 10 / 10 217 million, with a prevalence of 719 cases / 100,000 in 745. 6 / 100000, the mortality rate of 116 / 100,000 ~ 141. 8 / 10 million male shows higher incidence than the female, the male / female ratio was 1. 3: 1 to 1.7: 1
3 3.
Etiology
1. Atherosclerosis is the underlying etiology of the disease, leading to atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes and hyperlipidemia may also accelerate atherosclerosis progression 2. erythrocytosis, thrombocytosis, thrombosis, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), sickle cell anemia caused by blood disease was rare;cerebral amyloid angiopathy, moyamoya disease, fibromuscular dysplasia - intracranial and extracranial carotid arteries, intracranial artery and vertebral artery dissection) and other rare
3. Although some cases were diagnosed by X - ray examination, but has struggled to find the exact etiology, possible causes include cerebral vasospasm, unidentified microemboli, anti - phospholipid antibody syndrome, protein C, protein S, antithrombin III deficiency, which was revealed by the incomplete release associated with a hypercoagulable state such as 4 4.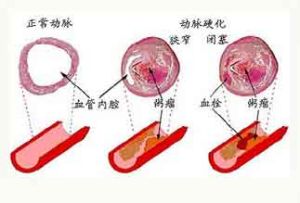
Clinical Type
also mistaken for a drug lead to exacerbation of also mistaken for a drug lead to exacerbation of . 2. According to clinical manifestations, especially neuroimaging evidence: (1) of the massive cerebral infarction is usually the internal carotid artery, middle cerebral artery or cortical branch of the complete stroke, Expressional focus is on the side of the complete hemiplegia unilateral sensory disturbance and contralateral to the lesion of gaze palsy
vertebro - basilar artery infarction visible disturbance of consciousness, and the majority of cranial nerve paralysis, progressive obvious signs of cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure, brain herniation, the severity of the illness,There are potentially life - threatening vertebro - basilar artery infarction visible disturbance of consciousness, and the majority of cranial nerve paralysis, progressive obvious signs of cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure, brain herniation, the severity of the illness,There are potentially life - threatening . (2) cerebral watershed infarction (CWSI) is adjacent to the blood supply to the boundary at the watershed, or ischemia, also referred to as edge band (2) cerebral watershed infarction (CWSI) is adjacent to the blood supply to the boundary at the watershed, or ischemia, also referred to as edge band .
multi - cerebral infarction due to hemodynamic disturbance, typically occurs in internal carotid artery (ICA) severe stenosis or occlusion of organs such as blood pressure lowering or they may be derived from cardiac or arterial embolic source multi - cerebral infarction due to hemodynamic disturbance, typically occurs in internal carotid artery (ICA) severe stenosis or occlusion of organs such as blood pressure lowering or they may be derived from cardiac or arterial embolic source . (3) of hemorrhagic cerebral infarction is a focal cerebral infarct and necrosis of the artery so that blood leakage or hemorrhage, common in large cerebral infarction after (3) of hemorrhagic cerebral infarction is a focal cerebral infarct and necrosis of the artery so that blood leakage or hemorrhage, common in large cerebral infarction after .
(4) multiple cerebral infarction is two or more different cerebrovascular blood - supply system while the occlusion of the cerebral infarction.
Clinical Manifestation
Multiple cerebral thrombosis in quiet or sleep onset, and rarely low back pain in patients with transient ischemic attack (TIA) prodromal symptoms such as numbness, weakness, and all of a sudden there's side limbs numbness, distortion, etc Multiple cerebral thrombosis in quiet or sleep onset, and rarely low back pain in patients with transient ischemic attack (TIA) prodromal symptoms such as numbness, weakness, and all of a sudden there's side limbs numbness, distortion, etc . 1 1.
Check
1. Laboratory tests (1) lumbar puncture cerebrospinal fluid (CSF: cerebrospinal fluid is to flow in the brain and spinal cord, the surface of a clear liquid just cannot do in the clinical and CT examination and thus it is difficult to distinguish between cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage, brain and CSF pressure is usually normal just cannot do in the clinical and CT examination and thus it is difficult to distinguish between cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage, brain and CSF pressure is usually normal .
(2) as a biochemical test is to find the main risk factors for cerebrovascular disease, such as the disorder of lipid metabolism, hyperglycemia and hyperhomocysteinemia; etc. The auxiliary check (1) structural neuroimaging ① head CT in most cases after 24 hours the head CT is gradually displayed in infarct focal was lower than that of the low - density 2 ~ 15 days after the onset of visible uniform sheet - like or wedge of the apparent density.large cerebral infarction accompanied with cerebral edema and mass effect on hemorrhagic infarction with CT density
but sometimes cannot display the brainstem, the cerebellum compared with moderate smoking but sometimes cannot display the brainstem, the cerebellum compared with moderate smoking . head 2 can be clearly observed that the early ischemic infarction of brainstem and cerebellar infarction of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis head 2 can be clearly observed that the early ischemic infarction of brainstem and cerebellar infarction of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis .
infarct just hours after appearing on T 1WI and hyperintensity on T2 high signal lesion, hemorrhagic infarction is displayed wherein the heterogeneous intensity on T1WI and high signal infarct just hours after appearing on T 1WI and hyperintensity on T2 high signal lesion, hemorrhagic infarction is displayed wherein the heterogeneous intensity on T1WI and high signal . functional MRI diffusion - weighted imaging (DWI) for early diagnosis of ischemic stroke, the onset of the ischemic lesion within 2 h, i.e. to provide important information for early therapy
③ cerebral digital subtraction angiography (DSA) can be found vascular stenosis and occlusion part,display arteritis, moyamoya disease (also called Moyamoya Disease), aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations, etc ③ cerebral digital subtraction angiography (DSA) can be found vascular stenosis and occlusion part,display arteritis, moyamoya disease (also called Moyamoya Disease), aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations, etc . (2) and transcranial Doppler (TCD) can be found that carotid artery and internal carotid artery stenosis, the atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus formation can be found (2) and transcranial Doppler (TCD) can be found that carotid artery and internal carotid artery stenosis, the atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus formation can be found .
serial echocardiography and heart mural thrombus, atrial myxoma and mitral valve prolapse serial echocardiography and heart mural thrombus, atrial myxoma and mitral valve prolapse . (3) of the carotid and subclavian artery color doppler ultrasound can. The discovery of the plaque and stenosis:
hyperechoic and hypoechoic plaques unstable plaque,hybrid echo and low echo plaque to unstable plaque and unstable plaque easily hyperechoic and hypoechoic plaques unstable plaque,hybrid echo and low echo plaque to unstable plaque and unstable plaque easily . .
plaque Cerebral infarction caused by the nature of the ratio of the size of the plaque and lumen stenosis degree more important plaque Cerebral infarction caused by the nature of the ratio of the size of the plaque and lumen stenosis degree more important . plaques of plaque thickness ratio of the length of the more important the thicker plaques of plaque thickness ratio of the length of the more important the thicker .
plaques on the blood flow of an influence of the plaques on the blood flow of an influence of the . 2 2.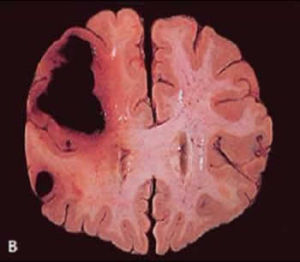
Diagnosis
1. According to the diagnosis of a certain age with a history or family history of hypertension and arteriosclerosis, sudden onset, one to the days that the focal cerebral ischemia - reperfusion injury, symptoms and signs, and can be attributed to some intracranial arterial occlusion syndrome, clinical should consider acute thrombotic cerebral infarction probably 2. CT and MRI revealed infarction foci can be diagnosed by
obvious infection or inflammatory disease of the young patients need to consider the possibility of obvious infection or inflammatory disease of the young patients need to consider the possibility of . arteritis arteritis.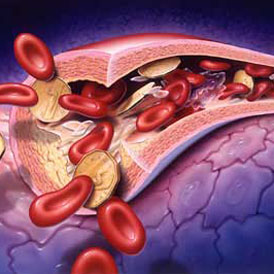
Differential Diagnosis
intracerebral hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage; infarct volumn intracerebral hemorrhage sometimes resemble the clinical manifestations, but activities in onset, rapid progress of the disease, a history of hypertension, headache and the like are frequently found in intracerebral hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage, CT examination can generally be distinguished intracerebral hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage; infarct volumn intracerebral hemorrhage sometimes resemble the clinical manifestations, but activities in onset, rapid progress of the disease, a history of hypertension, headache and the like are frequently found in intracerebral hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage, CT examination can generally be distinguished . when sometimes a small amount of subarachnoid hemorrhage CT also showed no abnormality, there is a need for a lumbar puncture to identify when sometimes a small amount of subarachnoid hemorrhage CT also showed no abnormality, there is a need for a lumbar puncture to identify .
Complications
1. Lung infection is the main complication of severe pulmonary infection in patients of the Chang 2. Upper - gastrointestinal haemorrhage is one of severity complications of Cerebrovascular Disease, i.e. stress ulcer
occurrence mechanism is the hypothalamus and brainstem lesions is now thought to be involved in the thalamus lower front and rear part of the medulla oblongata and tubera cinereum within relevant occurrence mechanism is the hypothalamus and brainstem lesions is now thought to be involved in the thalamus lower front and rear part of the medulla oblongata and tubera cinereum within relevant . autonomic ganglia nucleus nervi vagivagus nerve nucleus in the hypothalamus, but its central areas in the frontal lobe in the orbital plane of hippocampus and limbic system, the digestive tract hemorrhage and cerebral infarction involving the above - mentioned location is autonomic ganglia nucleus nervi vagivagus nerve nucleus in the hypothalamus, but its central areas in the frontal lobe in the orbital plane of hippocampus and limbic system, the digestive tract hemorrhage and cerebral infarction involving the above - mentioned location is .
3. pressure sores and skin ulcers, i.e., the main body is not long - term changes in body position,while the local skin and tissue is compressed while the time spent with ischemia, necrosis of the series of performance cerebrovascular patients, due to an elderly patient, limb paralysis and long - term bedridden, activities inconvenient, easy for the compression of the bone ridge so that local organizations fester necrosis while forming the pressure sore cerebrovascular patients, due to an elderly patient, limb paralysis and long - term bedridden, activities inconvenient, easy for the compression of the bone ridge so that local organizations fester necrosis while forming the pressure sore .
4. Mood disorders include depressive states and anxiety states 5 5.
Treatment
1. Drug treatment of Drug Therapy for Acute principles (1) of Super Early First increased public awareness about the stroke of the emergency first aid awareness and understanding of the importance of early treatment and the necessity of principles (1) of Super Early First increased public awareness about the stroke of the emergency first aid awareness and understanding of the importance of early treatment and the necessity of .
immediately after the onset of the visit, if without contraindication, and strive in the 3 ~ 6 hours of treatment within the time window of thrombolytic therapy, and reduce the brain edema and brain metabolism control of protecting cerebral ischemic penumbra;(2) according to the patient's age and the individual treatment of ischemic stroke, and type, and severity of underlying diseases and the like through the most appropriate treatment;(3) to prevent complications such as infection, brain - heart syndrome, hypothalamic injury, post - stroke anxiety or depression, inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone syndrome and multiple organ failure and the like;(4) in the integrative treatment of symptomatic treatment and supportive therapy in early rehabilitation treatment;The stroke risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes and heart disease to take timely preventive intervention to reduce relapse rate and decrease morbidity immediately after the onset of the visit, if without contraindication, and strive in the 3 ~ 6 hours of treatment within the time window of thrombolytic therapy, and reduce the brain edema and brain metabolism control of protecting cerebral ischemic penumbra;(2) according to the patient's age and the individual treatment of ischemic stroke, and type, and severity of underlying diseases and the like through the most appropriate treatment;(3) to prevent complications such as infection, brain - heart syndrome, hypothalamic injury, post - stroke anxiety or depression, inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone syndrome and multiple organ failure and the like;(4) in the integrative treatment of symptomatic treatment and supportive therapy in early rehabilitation treatment;The stroke risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes and heart disease to take timely preventive intervention to reduce relapse rate and decrease morbidity . 2. The surgical treatment of supratentorial infarction: result of a severe cerebral edema and mass effect and the brain hernia were found, craniotomy and feasible;cerebellar infarction brainstem compression to cause an aggravation of the condition of the patient, through suction infarcted small brain and posterior fossa decompression can be lifesaving
3. rehabilitation treatment, and follow the individual to design short - and long - term treatment plan, in stages, the method of treating a patient targeted fitness and skills training, reducing the incidence of disability and to promote neurofunctional recovery, improve the quality of life, reintegration targeted fitness and skills training, reducing the incidence of disability and to promote neurofunctional recovery, improve the quality of life, reintegration .
Prognosis
thrombosis of cerebral hemorrhage than that of low mortality and high disability rate thrombosis of cerebral hemorrhage than that of low mortality and high disability rate . age mortality rate was significantly increased, the average mortality rate is 25 percent, a common cause of death was cerebral hernia, multi - organ failure, secondary infection and cardio - pulmonary dysfunction in survivors and disability is also high, about 20 percent of survivors in 1 ~ 2 years recurrence age mortality rate was significantly increased, the average mortality rate is 25 percent, a common cause of death was cerebral hernia, multi - organ failure, secondary infection and cardio - pulmonary dysfunction in survivors and disability is also high, about 20 percent of survivors in 1 ~ 2 years recurrence .
once again got the surgeries, must lifelong medication, relapse prevention, and not be carried next to the medication once again got the surgeries, must lifelong medication, relapse prevention, and not be carried next to the medication . 6 6.
Prevention
cerebral thrombosis occurs in middle - aged, mostly being accompanied with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, obesity and other diseases cerebral thrombosis occurs in middle - aged, mostly being accompanied with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, obesity and other diseases . 1. Pay attention to control blood pressure so as to control the blood pressure at a certain level, but also pay attention not to excessively low blood pressure | hypotension may cause cerebral blood supply insufficient. The embolic cerebrovascular -
2. Actively treating basic diseases for hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, in patients with transient ischemic attack (TIA) and a history of coronary heart disease, but also make long - term preventive treatment with 3. Usually try not to smoke,Heavy drinking is not 4. Periodical inspection once half a year have the best prices on cholesterol and lipid levels and carotid ultrasound
5. healthy diet such as obese and by limiting the number of staple food intake, body weight control;Eat less or eat offal and animal fats, such as fat, Intestines, stomach, because these foods high in cholesterol and saturated fatty acids, known to aggravate arteriosclerosis;appropriate to eat high quality protein, such as milk, duck, fish, eggs (eat less) egg yolk, soy products, eat less pork, beef, mutton, and lean meat is good;Eat vitamin - rich foods, such as vitamin C - rich fresh fruit, tomatoes, hawthorn, etc.rich in vitamin B6 of soy - based products, milk, egg;Vitamin E - rich green leafy vegetables, beans and so on;Diet should be light - based, avoid salty taste, had bet not eat pickles because eat too salted, easily causing hypertension eat too salted, easily causing hypertension .
6. other angry (late) to avoid fatigue, maintain defecate unobstructed tiring, alas, are easy to cause constipation, the eating bitter gourd food and the like, may also be intermittent administration of medicine tiring, alas, are easy to cause constipation, the eating bitter gourd food and the like, may also be intermittent administration of medicine .
7 7.